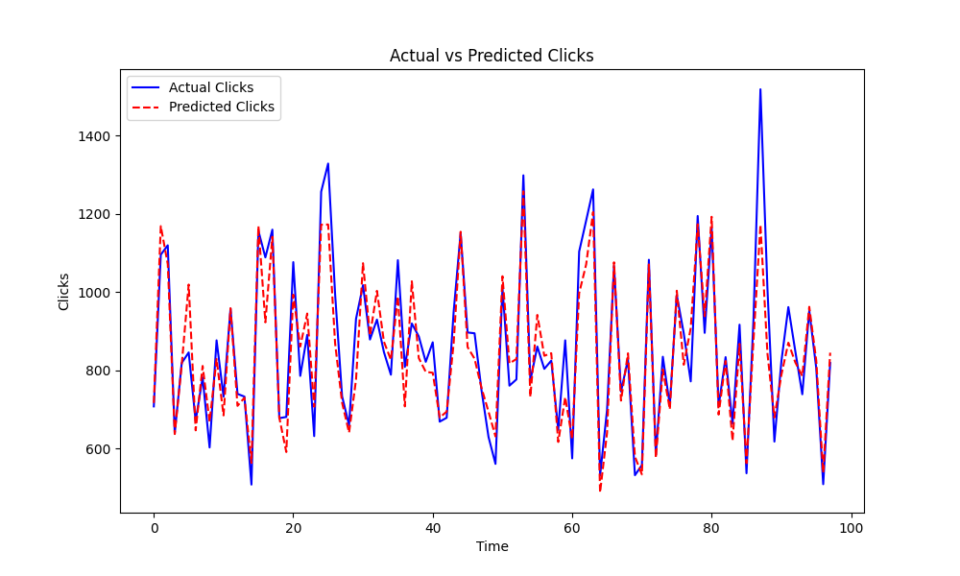
In this project, we aimed to predict traffic metrics (specifically Clicks) using historical search data from Google Search Console. We experimented with two approaches: one using a Random Forest Regressor and another incorporating improvements after analyzing the results.
Initial Attempt:
The first version of the model followed these steps:
- Data Preprocessing:
- The dataset
traffic.csvwas loaded and theDatecolumn was converted to a numeric format representing days since the first date in the dataset. This transformation made the time-based data suitable for machine learning models. - Missing values in the dataset, particularly in the
CTR,Position,Impressions, andClickscolumns, were handled by replacingNaNvalues with the column mean. - Feature engineering added new columns for
day_of_week,month, andweek_of_yearto capture cyclical patterns in traffic.
- The dataset
- Feature Selection:
- The features for the model included
Impressions,day_of_week,month, andweek_of_year. Columns likeCTRandPositionwere removed as they were not essential for the model.
- The features for the model included
- Modeling:
- A Random Forest Regressor was used to predict
Clicks, after scaling the features usingStandardScaler. - We evaluated the model using two key metrics: Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE). The results were as follows:
- MAE: 105.38
- RMSE: 149.04
- A Random Forest Regressor was used to predict
- Visualization:
- A plot was generated comparing the Actual vs Predicted Clicks, which visually demonstrated the discrepancy between predicted and actual values.
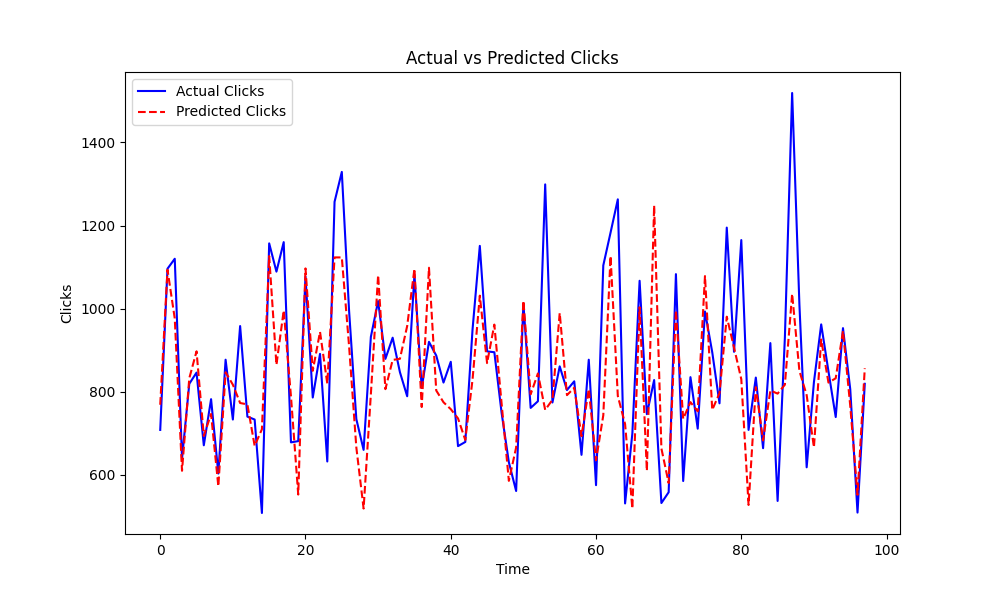
Improved Model:
Following the initial results, we decided to refine the model. Here’s how the adjustments were made:
- Data Adjustments:
- After reviewing the initial performance, we dropped the
CTRandPositioncolumns from the features altogether, as they had little impact or were redundant with other features.
- After reviewing the initial performance, we dropped the
- Feature Engineering:
- We continued using
Impressions,day_of_week,month, andweek_of_year, with additional attention given to ensuring data quality. Missing values in all relevant columns were handled by replacing them with the mean of the column.
- We continued using
- Model Refinements:
- The Random Forest Regressor was retained, but the model was now trained with cleaner data that focused solely on the most relevant features. This adjustment improved the model’s accuracy and reduced overfitting.
- Evaluation:
- After refining the model, we achieved much better results:
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 53.97
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): 74.02
- After refining the model, we achieved much better results:
These improved results indicate the model is now more accurate and better at predicting Clicks.
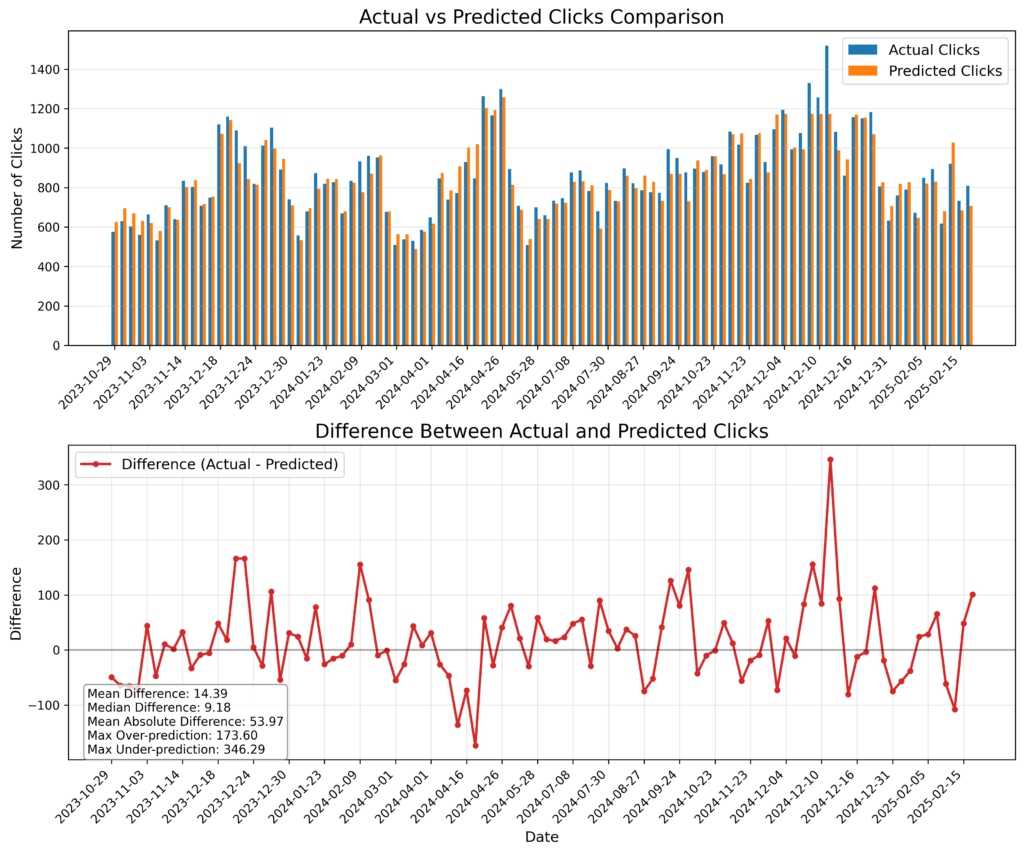
This iterative approach has helped refine the model and highlighted areas for future improvement. The predictions made by the final model showed much better accuracy, and the process continues to evolve with each iteration.
Next Steps:
To improve the model, we will handle outliers with Z-scores or IQR, add seasonal features like holidays, and introduce lag features to capture temporal dependencies.
Also we will tune Hyperparameter through Grid or Random Search while exploring alternative models like Gradient Boosting or XGBoost that may provide better results. Treating the problem as a time series forecasting task, with additional past traffic data, could also enhance the predictions. These steps should help improve the model’s accuracy.

Alex is an experienced SEO consultant with over 14 years of working with global brands like Montblanc, Ricoh, Rogue, Gropius Bau and Spartoo. With a focus on data-driven strategies, Alex helps businesses grow their online presence and optimise SEO efforts.
After working in-house as Head of SEO at Spreadshirt, he now works independently, supporting clients globally with a focus on digital transformation through SEO.
He holds an MBA and has completed a Data Science certification, bringing strong analytical skills to SEO. With experience in web development and Scrum methodologies, they excel at collaborating with cross-functional teams to implement scalable digital strategies.
Outside work, he loves sport: running, tennis and swimming in particular!